Synthesis of 2 alpha-heteroarylalkyl active vitamin d3 with therapeutic effect on enhancing bone mineral density in vivo
Matsuo, M., Hasegawa, A., Takano, M., Saito, H., Kakuda, S., Chida, T., Takagi, K., Ochiai, E., Horie, K., Harada, Y., Takimoto-Kamimura, M., Takenouchi, K., Sawada, D., Kittaka, A.(2013) ACS Med Chem Lett 4: 671-674
- PubMed: 24900728
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ml400098w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ITE, 4ITF - PubMed Abstract:
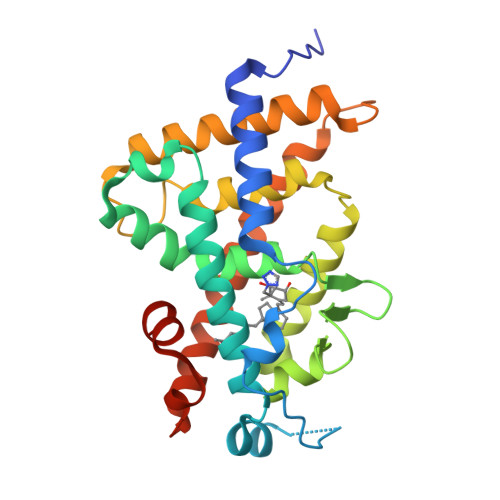
2α-Heteroarylethyl-1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 analogues, which were designed to form a hydrogen bond between Arg274 of human vitamin D receptor (hVDR) and a nitrogen atom of the heteroaromatic ring at the 2α-position, were synthesized. Among them, 2α-[2-(tetrazol-2-yl)ethyl]-1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 showed higher osteocalcin promoter transactivation activity in human osteosarcoma (HOS) cells and a greater therapeutic effect in ovariectomized (OVX) rats, osteoporosis model animals, on enhancing bone mineral density than those of active vitamin D3. X-ray cocrystallographic analysis of the hVDR-ligand complex confirms that the new hydrogen bond formation stabilized the complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Teikyo University , Itabashi-ku, Tokyo 173-8605, Japan.